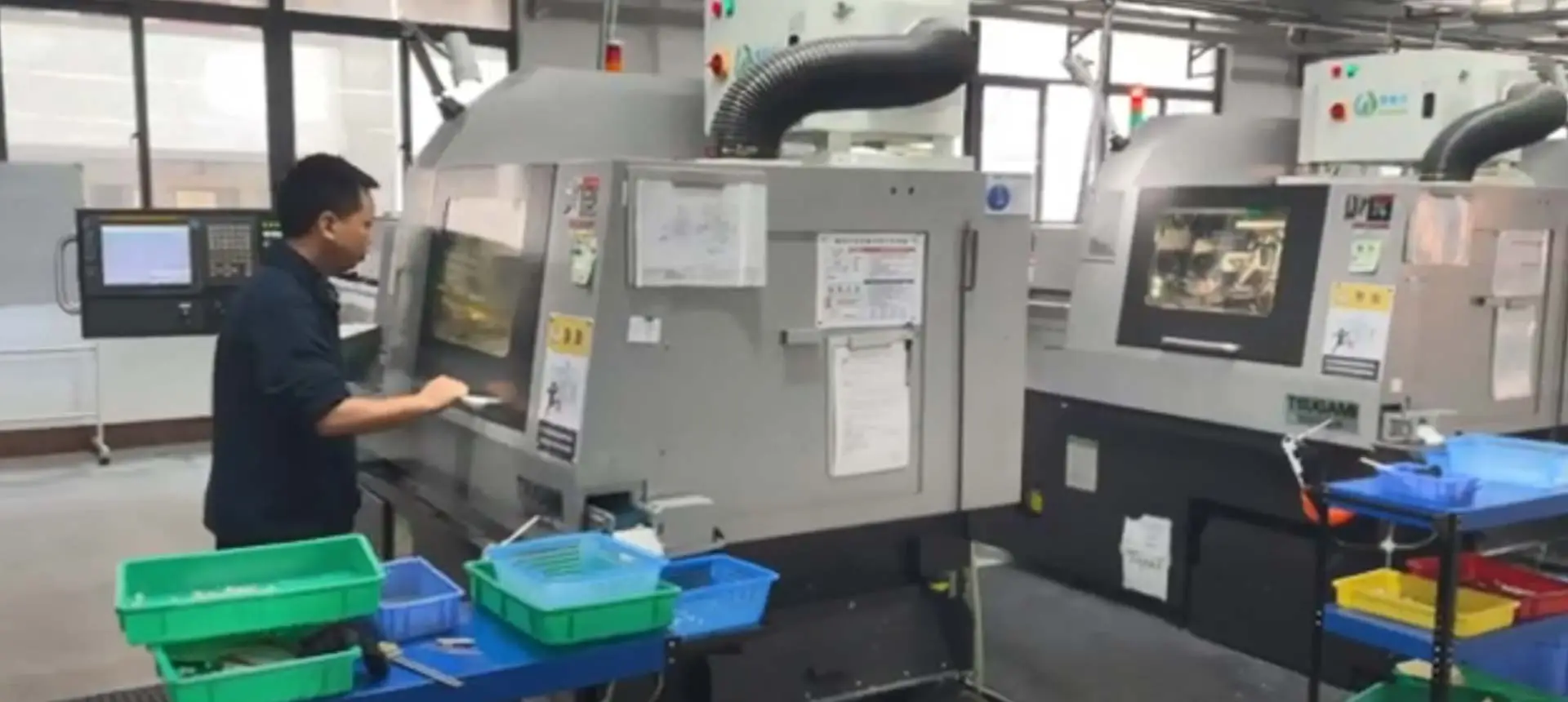
در شرکت ما، ما از یک فرایند بسیار موثر استفاده می کنیم تا بخش های ماشین سازی سی ان ان ای که با شرایط مشتری هامون برآورده بشه این یک نمای کلاسی از فرایند ما پیروی می کنیم:
طراحی و برنامه نویسی: مهندسین ماهر ما با آخرین نرم افزار برای طراحی و برنامه ریزی این قسمت کار می کنند. مطمئن شدن که مشخصات لازم و تحمل مورد نظر قرار بگيره
انتخاب مادی : ما با دقت مادهٔ مناسب را انتخاب می کنیم ، با توجه به قدرت ، پایداری و خصوصیات دیگری .
ماشین سی ان این که شامل حذف مواد زیادی از کارگر برای ایجاد شکل نهایی قسمت است.
بازرسی کیفیت: تیم ما قسمت ها را در هر مرحله از فرآیند بررسی می کنند با استفاده از آخرین تکنولوژی و تجهیزات برای مطمئن شدن هر بخشی از استاندارد کیفیت مورد نیاز قرار داره
به پایان رسیدن: ما گزینه های پایانی پیشنهاد می کنیم، از جمله شن شیرین، لاش، انواع و پوشش، براي افزايش ظاهر و عملکردي بخش ها.
بسته بندی و انتقال: ما با دقت قسمت ها رو جمع می کنیم تا رسیدن امن اونا رو به مشتری هامون برسونیم.
با تعهد ما به کیفیت، کارایی و رضایت مشتری ما اعتبار به عنوان يک اعتماد به بخش هاي ماشين هاي سفارشي سي ان اي ان اي ساختيم اگر شما پروژه ای دارید که نیاز به قسمت های ماشین با کیفیت بالا دارد، لطفا با ما تماس بگیرید تا در مورد شرایط شما و چگونه می توانیم کمک کنیم.
توصیف | CNC میلینگ | چرخش CNCName |
مواد ها | آلومینیوم/ کو / فولاد / بدی | آلومینیوم/ کو / فولاد / بدی |
اندازۀ بیشینۀ جزء | هزار میلی متر | ۰۰۰ میلی متر * ۶۰۰ میلی متر |
زمان سرخ استاندارد | ۴ روز تجاری | ۴ روز تجاری |
تحمل) ± فرم ( | تنها زدن: تا ± ۰٫۰۲۵ میلیم با برش سیم یا EDM: تا ۰٫۰۰۲ میلیم | تا ± ۰. ۰. ۰. |
اطمینان کیفیت | ISO 9001, ISO 45001: 2010 بازرسی های تدارک پروژۀ اندازۀ CMM و 2D گزارش های بازرسی بازرسی تابعی نمونه بندی سفارشی | ISO 9001, ISO 45001: 2010 بازرسی های تدارک پروژۀ اندازۀ CMM و 2D گزارش های بازرسی بازرسی تابعی نمونه بندی سفارشی |
دقت بالا و دقت: با ماشین CNC، قطعات می تواند با تحمل بسیار محکم و دقت بالا تولید شود، فراهم کردن
گستره وسیع از مواد: ماشین CNC می تواند با مواد مختلفی از جمله فلز، پلاستیک، چوب استفاده شود. و ترکيب ها.
هزینه برای تولید بزرگ: ماشین CNC برای تولید جلدی بالا ایده است زیرا قادر به تولید مقدار زیادی از قطعات به هزینه پایین تر در هر قطعه می باشد.
طبیعت خودکار ماشین CNC به این معنی است که تولید را می توان به صورت موثرتر انجام داد، بدون احتياج به مداخله دستي، نتيجه سريع تر از زمان توليد.
ماشین CNC می تواند برای تولید اجزای پیچیده با شکل پیچیده و هندسی استفاده شود، اين رو براي يکي از برنامه ها مناسب مي کنه
در قلمرو تولید دقیق، کنترل عددی کامپیوتر (CNC) ماشين به عنوان يک شگفت انگيز تکنولوژي ايستاده که صنعت توليد رو انقلاب کرده. ماشين سازي سي ان اين اجازه دادن تولید بسیار دقیق و کارآمد قسمت ها و اجزای پیچیده فرایند های ماشینی CNC تحت HHC گسترش های کاربردی متفاوتی و ویژگی های پردازشی دارند. زیر طبقه بندی و معرفی جزئیاتی را فراهم می کند.
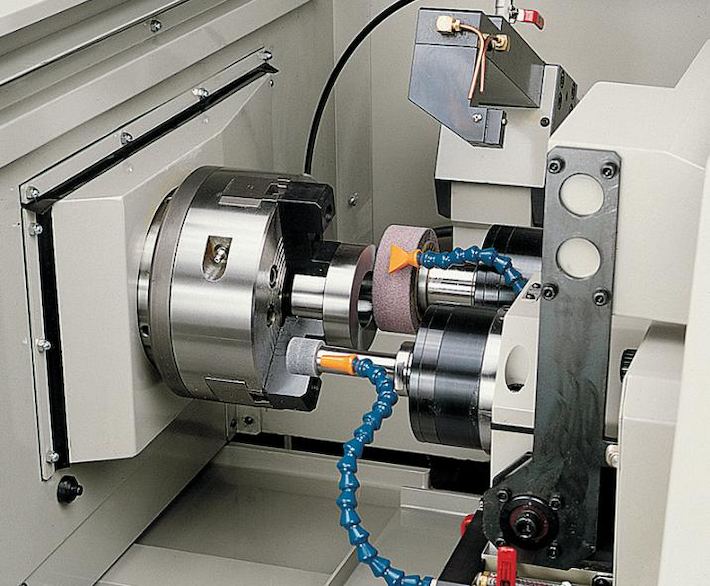
یکی از رایج ترین انواع ماشین CNC، یکی از ابزارهای چرخش برای حذف مواد از یک کاری استفاده می کند. این ماشین می تواند در چند تبر را حرکت کند و یک گستره گسترده از شکل ها، لوله ها و سوراخ ها ایجاد کند. از اجزای ساده تا اولیه های پیچیده، میلینگ بسیار قابل پذیر است و در صنایع هایی مانند هوا فضا، خودرویی و الکترونیکی استفاده می شود.
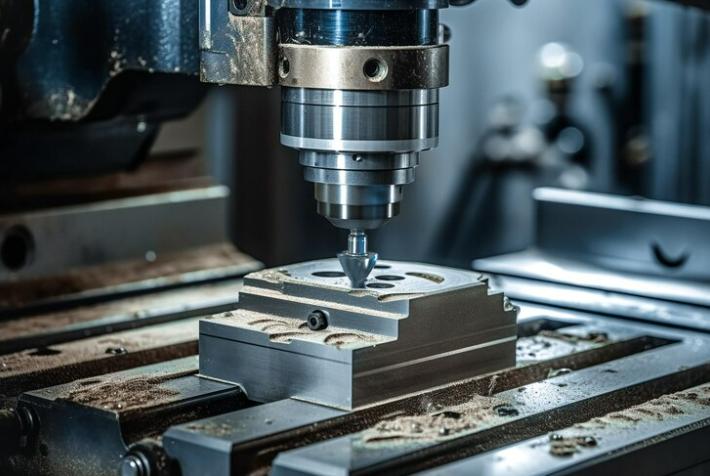

در تغییر عملیات، کارگر می چرخد در حالی که ابزار بریدن آن را به فرم مورد نظر شکل می دهد. این نوع ماشین CNC برای ایجاد مؤلفه های سیارکهای مثل شیشه ها، ضربه ها و اسب ها ایده آل است. چرخش دقیق یکی از روند های تولید است که کاربرد های مختلف را فراهم می کند.
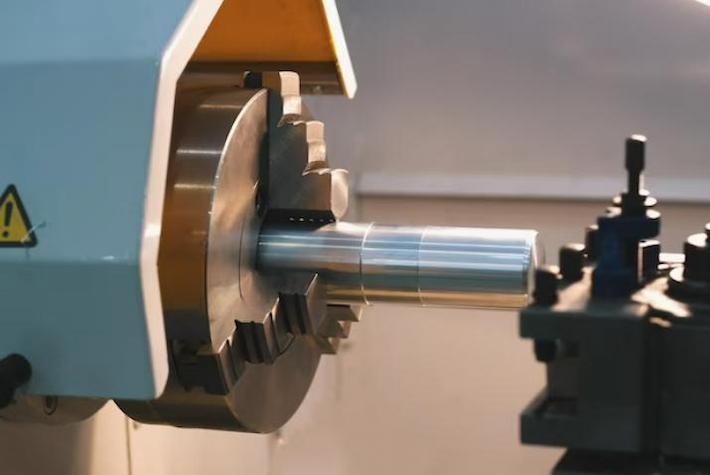

همانطور که نام نشان می دهد، ماشین های حفاری CNC برای ایجاد سوراخ های کاری طراحی شده اند. این ماشین ها از بیت های متحرک برای حذف ماده استفاده می کنند، و آنها در تولید اجزایی که نیاز به سوراخ های دقیق و یکنواخت دارند، حیاتی هستند. صنایع مانند ساختمان، فلز کار کردن و الکترونیکی بسیار شدیدا به حفاری CNC برای نیازهای تولیدشان بسیار تکیه می کنند.
وقتی دقیق و پایان سطح زیادی باشد، خریدن CNC در بازی می شود. این روش برای حذف ماده و تحمل محکم استفاده می کند. پوشش CNC در تولید ابزار، کپک ها، ضروری است. و اجزاي دقيقي بالايي توي دستگاه هاي پزشکي و مهندسي هوا فضايي استفاده ميشه

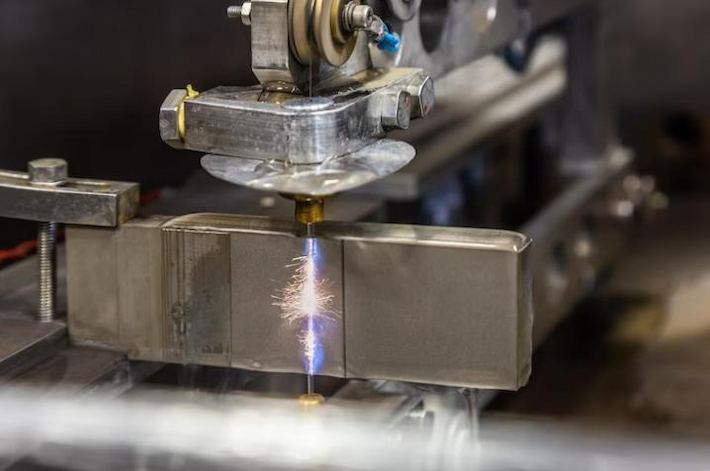
EDM یک روش غیررسمی CNC است که از تخلیه های الکتریکی برای شکل مواد استفاده می کند. با جرقه های الکتریکی با دقت کنترل شده، EDM می تواند شکل پیچیده و پیچیده را با دقت بالا ایجاد کند. این تکنیک مخصوصا برای فلز های سخت مفید است که برای ماشین با روش های سنتی چالش کننده است. برای مثال ، ما از ماشین تخلیه الکتریکی (EDM) استفاده می کنیم تا قالب هایی را برای قالب ها

برش لیزر CNC شامل استفاده از لیزری برای بریدن از مواد می شود و لبه های دقیق و تمیز می شود. این روش به طور گسترده ای در ساخت سازی اجزای فلزات برای صنایع از خودرو تا الکترونیکی مصرف کننده استفاده می شود. سطح بالای دقت و سرعت باعث می شود CNC لیزر یک فرایند بسیار ارزشمند در تولید مدرن شود.

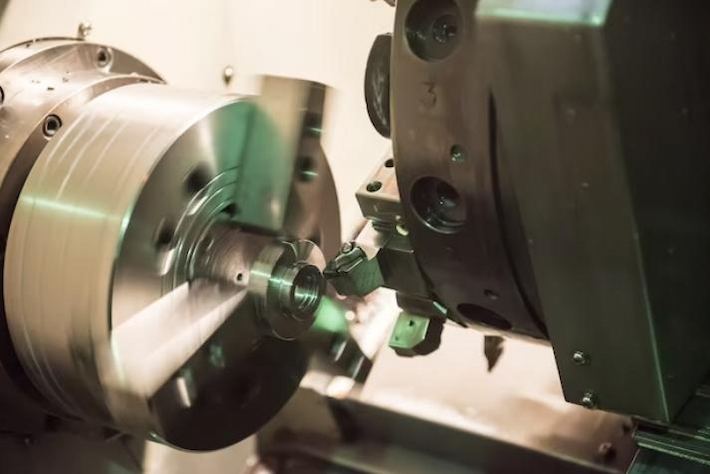
در منظره ای که همیشه تولید می شود، دو تکنولوژی بریدن به عنوان پیشین ها ظاهر شده اند: ماشين سازي CNC و چاپ 3 بعدي هر روشی بیایید به پیچیدگی های ماشین سی انC و چاپ سه بعدی بررسی کنیم، با مقایسه های ویژگی ها، مزیت ها و محدودیت هایشان.

ماشینی CNC (Computer Numerical Control) یک فرایند تولید کمتری است. این موضوع شامل برداشتن مواد از یک کاری برای رسیدن به شکل مورد نظر است. این فرایند از طراحی کامپیوتر (CAD) و نرم افزار تولید کامپیوتر (CAM) برای کنترل دقیق حرکت ابزارهای برش استفاده می کند.
ماشين سازي سي ان اين ميتونه تحمل محکم رو به دست بياره و جزئيات پيچيده اي توليد کنه که اون رو براي برنامه هايي که دقت بهتره مثل صنایع های هوا فضایی و پزشکی. ماشين سازي سي ان اين این مواد می تواند گسترده ای از جمله فلز، پلاستیک و ترکیب ها به دست آورد. این یک انتخاب ترجیح می دهد برای صنایع هایی که نیازمند و قوی در اجزای آنها دارند. ماشین CNC مناسب است هم برای نمونه و هم مقیاس بزرگ. در حالی که زمان برپایی برای ماشین CNC می تواند طولانی تر از چاپ سه بعدی باشد، در تولید کیفیت بالایی، قسمت هاي عملياتي ماشین CNC یک پایان بالای سطح در مقایسه با بسیاری از تکنولوژی چاپ 3D فراهم می کند. این یک انتخاب ایده آل برای اجزایی که به یک سطح برقی یا نرم نیاز دارد.
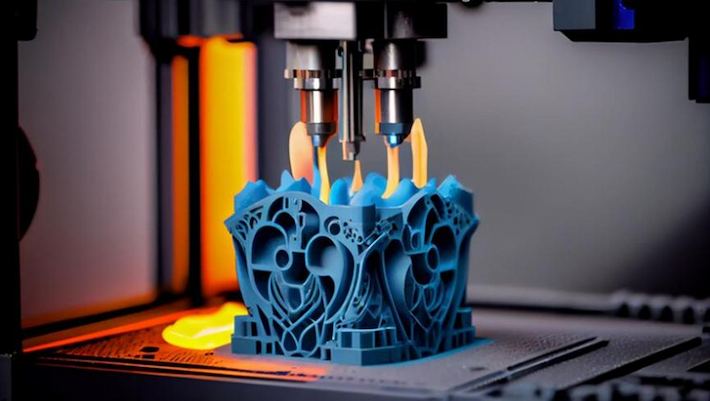

چاپ سه بعدی ، یا تولید اضافی ، اشیاء را ایجاد می کندلایه به لایه از یک مدل دیجیتال. این شامل گذاشتن مواد در یک الگو خاص برای ایجاد یک شیء سه بعدی است. این فرایند بسیار متفاوت است و به هندسی پیچیده اجازه می دهد.
چاپ سه بعدی از مواد های مختلفی از جمله پلاستیک، فلز، سرامیک و حتی ماده های بیولوژیک را پشتیبانی می کند. انتخاب های مادی ادامه دارد و احتمالات جدید برای صنایع مختلف را باز می کند. چاپ سه بعدی در نمونهٔ اولیپیگری سریع و مناسب است برای هندسی های پیچیده که ممکن است برای ماشین CNC چالش کننده باشد. با این حال، ممکن است با سرعت ماشین CNC با تولید مقیاس بزرگی مطابقت نداشته باشد. در مورد هزینه، مخصوصا برای تولید و نمونه ی اولیه چاپ سه بعدی می تواند به دلیل کاهش هدر رفته و برپایه های ساده تر ارائه دهد. چاپ سه بعدی برای قابلیت های سفارشی اين اجازه ميده که طراحي هاي منحصر بفرد و شخصي بدون اينکه نياز به ابزار اضافي داشته باشه اين رو براي توليد يک يا يک دسته کوچک ايده آل مي کنه
در کل، انتخاب بین ماشین CNC و چاپ 3D بستگی به عوامل مثل مواد، نیازهای دقیق، مقیاس تولید دارد و پيچيدگي پروژه ،براي اجراي توليد هاي بزرگتر ، ماشين سي ان اي اس ، بهتر از دقت و مواد بسيار زيادي هست در حالی که چاپ سه بعدی در اولیپیگری سریع و برنامه های طراحی پیچیده درخشند.
.کتيون
ماشینی CNC (Computer Numerical Control) نقش مهمی در تولید اجزای دقیق با کیفیت بالا دارد. زیر مرحله های عمومی و جزئیات تولید فلنج های ماشین CNC است:

مرحله های فرایند برای فلنج های با ماشین CNC:
طراحی و مدل سازی:
پیش از تولید مواد CNC، طراحی CAD (طراحی کامپیوتر-Aided) ضروری است. مهندس هاي طراحي از نرم افزار CAD استفاده ميکنن تا يک مدل سه بعدي از فلنج رو بسازن و راه هاي ماشين
آماده سازی مادی :
انتخاب مواد خام مناسب، معمولاً فلزات ( مانند فولاد بی لکن، آلومینیوم و غیره). انتخاب مادی بستگی به هدف فلانج، محیط کاری و نیازهای عملیات دارد.
فرآیندهای ماشینی:
آ.
از ابزار های بریدن در ماشین های CNC استفاده کنید برای انجام دادن سختگیری، تقریبا شکل به شکل کلی کار کاری.
هدف سختگیری سریع حذف مواد زیادی است و شکل نهایی تقریباً باقی مانده است.
ب. نیمه پایان:
استفاده از ابزارهای مختلف برای پایان دادن کار کار، بیشتر به شکل نهایی نزدیک می شود.
سرعت را کاهش دهید تا سطح رو بهبود بیاورید.
C. در حال پایان:
از ابزارهای کوچک برای برش دقت نهایی استفاده کنید، به ابعاد نهایی و نرم سطح.
به پایان دادن اغلب شامل استفاده از ابزارهای کوچکتر برای افزایش دقت ماشینی است.
D. ماشین و برش رشته:
استفاده از ابزارهای تخصص برای ماشین چاله و برش نخ استفاده کنید تا اطمینان داشته باشد که فلنج مشخصات طراحی شود.
بازرسی و کنترل کیفیت:
بعد از هر گام ماشینی، بازرسی هایی انجام می دهد تا اطمینان داشته باشد ابعاد کارگر، شکل و کیفیت سطح بر روی نیازهای مشخصی. روش های عمومی بازرسی شامل اندازه گیری مختصات، آزمایش خشونت سطح و آزمایش فراسنیکی است.
درمان سطح:
بستگي به نيازهاي ، درمان هاي سطحي مثل برق ، شني يا پوست براي افزايش ظاهر و مقاومت تبديل ميشه
بسته بندی و تحویل:
بعد از تکمیل ماشین و بازرسی، فلنج ها را بر اساس نیازهای مشتری بسته بندی کنید و به تحویل رسیدگی کنید.
CNC) کنترل عددی رایانه ( ماشین یک فرایند تولید سازی است که نرم افزاری از پیش برنامه نویسی کامپیوتر در حرکت ماشین و ابزار ها را کنترل می کند. این فرایند اجازه می دهد که اعضای بسیار دقیق و پیچیده از مواد مختلف، از جمله فلز و پلاستیکی بسیار ایجاد کند. ماشین CNC به طور گسترده در صنایع مانند خودکار، الکترونیک و هوا فضا استفاده می شود.
چرخش CNC برای تولید قطعات سفینه یا گردی ایده آل است، مانند شیشه ها، بوسیله ها، پیچ ها و پین ها. معمولاً برای اجزای استفاده می شود که به سطح های بلند و صافی نیاز دارند. صنایع از قبیل ماشین ، پزشکی و الکترونیکی از سود می بردآلومینیوم چین قسمت هایی تبدیل شده.
دنبال تهیه کننده با تجربه وسیع ، تجهیزات مدرن و تعهد قوی به کنترل کیفیت . گواهی هایی مانند ISO 9001 و IATF 16949 نشان می دهد که مطابقت با استاندارد صنعت است. همچنین عواملی مانند ظرفیت تولید، زمان های سرپوش و بررسی مشتریان را در نظر بگیرید.
در اچ اچ اچ.چ.چ.ما قطعات دقيقي با تحملهاي محکم به اندازه ي .0.01 ميليمتري ارائه ميديم حتی پیچیده ترین اجزای دقیق بالا رو مطمئن میکنه تجهیزات پیشرفته ما به ما اجازه می دهد که پای بندی رو حفظ کنیم و به شرایط خاص هر پروژه برسیم .
زمان های سرب بر اساس پیچیدگی و مقدار بخش ها متفاوت است. ولي ما معمولا بخش هاي ماشين سازي سي ان ان اي رو در عرض 1 تا 4 هفته تحويل ميديم ما همچنین خدماتی به سرعت برای پروژه های فوری برای کمک به مشتریان ما برای رسیدن زمان محکم


